Explain How Do We See Different Colours of an Object
This video provides a general overview on how we see color. All the colors we perceive are an effect of light.

How We See In Color 8th Grade Science
The seemingly colorless sunlight actually contains all the colors we can see but at different wavelengths.

. Objects dont have any color. When a beam of white light falls on an object it absorbs certain wavelengths of light and reflects the other which is responsible for its colour. Many objects contain atoms capable of either selectively absorbing reflecting or.
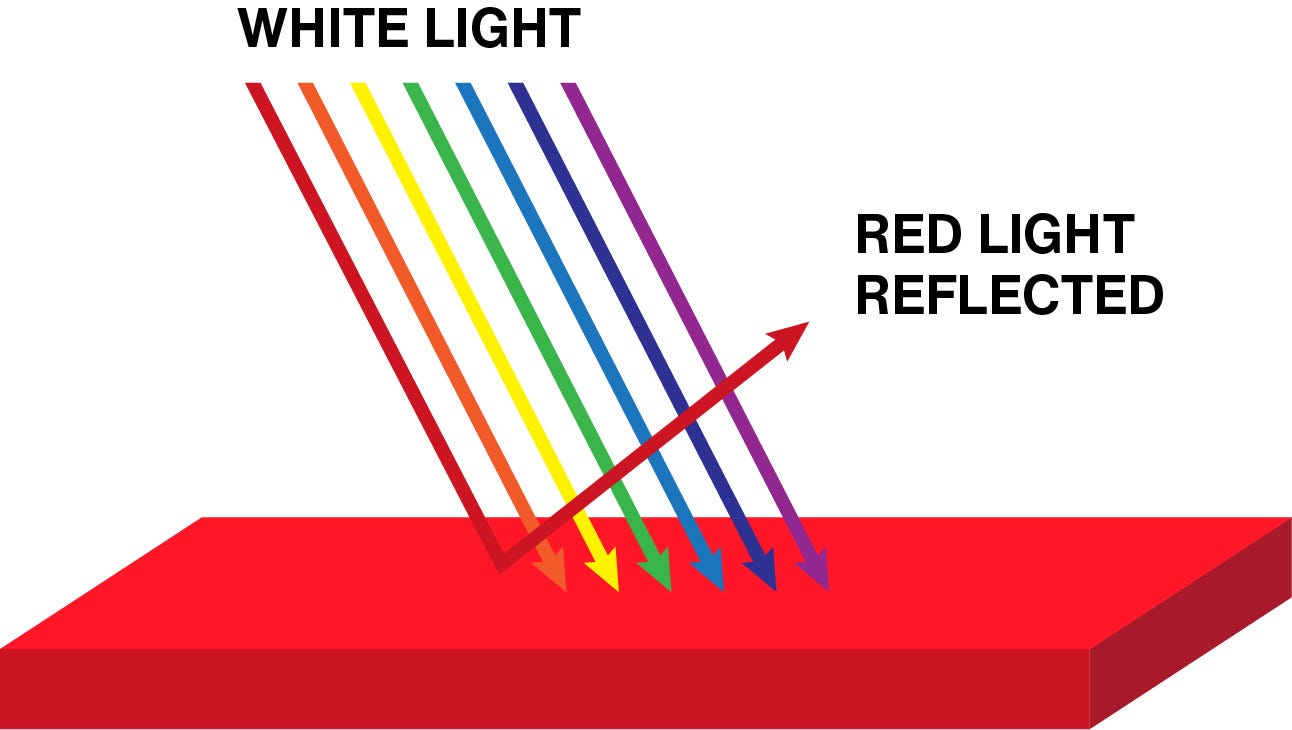
Objects appear coloured because of the way they reflect light. Light doesnt have any color. When you see objects you just receives light reflected or refracted from those objects which is perceived by your eye as color.
We would like to use color to tell things apart but the only thing that you really know about the color of an object is the three-number code that it generates in your cones. We perceive things to be a certain color because of the way our eyes sense the various frequencies of light reflected off of them. Ii This is because they do not possess some cone cells in their eye that respond to certain colours eg.
Red green and blueThey can be combined in different ways. The ones it reflects are the ones we see as color. White light is composed of radiation of all colors.
Up to 24 cash back How do we see Colors. In addition to the names referenced at the end of this v. In fact color itself is light of a particular wavelength reflected.
I The colour of an object depends upon the wavelength of light it reflects. A white ball looks that way because it. Sunlight is a mixture of all colours of light which combine to form brilliant white light.
Photons are absorbed by the electrons of the atoms that compose the molecules of an object. When an object receives light it absorbs some wavelengths and reflects others. The colors perceived of objects are the results of interactions between the various frequencies of visible light waves and the atoms of the materials that objects are made of.
Have you ever wondered how we see color. Our brain is responsible for deciding what color we are seeing based mainly on one factor. Dispersion of white light by a prism into a spectrum The spectrum.
Scientists explain that color in part is for object recognition. The light that comes through our eyes. A person often recognizes certain objects due to.
It means that any two sets of light rays that make your cones respond the same way will look identical even if they contain quite different wavelengths. Eye contains three types cells cones redblue green these. In other words when we see colours we are really seeing light of different wavelengths.
Light has different wavelengths and objects absorb and reflect certain wavelengths. Red-green colour blind person does not possess red and. If a material absorbs a certain frequency of light that frequency will not be reflected so its color will not be perceived by the observer.
Color is completely a phenomena of your eye. The colours we see are the wavelengths that are reflected or transmitted. With flashlights filters le.
Objects appear different colours because they absorb some colours wavelengths and reflected or transmit other colours. When light hits an object some is absorbed and some reflects eg. The absorption and reflection of light waves by various materials results in human perception of color as follows.
Here are the answers First you need to understand that light is nothing but electromagnetic wave there is nothing like color associated with any light. The light that we see is made up of many different colours. Join Rebecca Emerich Educational Outreach Manager as she uses everyday objects to explain absorption and reflection of light.
So tomatoes are red because the pigment atoms in the skin absorb photons of all energies except those that correspond to red. When a person views an opaque coloured object it is only the light reflected from the object that can activate the visual process in the eye and brainBecause different illuminants have different spectral energy distributions as shown in the figure a given object in these illuminations will reflect different energy distributions. The perception of colour Colour effects.
There are three primary colours. The color of an object has to do with the waves of visible light that it reflects. For example a red shirt looks red because the dye molecules in the fabric have absorbed the wavelengths of light from the violetblue end of the spectrum.
This means that the light leaving the prism is spread out into its different colours a process called dispersion. Most materials absorb light of some frequencies and reflect the rest. The color statistics of objects are not random.
This is determined by the arrangement of electrons in the atoms of that substance that will absorb and re-emit photons of particular energies according to complicated quantum laws. Colours only exist in the virtual construct our brain creates. When sunlight falls on an object the surface of the object absorbs some of the light and reflects the rest of it.
Red light has the longest waves orange is slightly shorter and so on. Whatever Wavelength of light is not absorbed by the electrons is reflected and its this Wavelength that we perceive as the color of the object as our Cones absorb the reflected light. Some surfaces reflect all of this light while others absorb some of the colours.
The colour of light depends on how long its waves are so we see different colours because each colour has a different wave length. The colour of an object is the wavelengths of light that it reflects. Violet has the shortest wavelengths.
If an object only reflects a certain wavelength of light and that wavelength is not present it appears black in our perceptions.

How We See In Color 8th Grade Science

Timeline Photos Qmi Agency Graphics Dept Eye Retina Color Therapy Mind Body
No comments for "Explain How Do We See Different Colours of an Object"
Post a Comment